Publications
2026
-
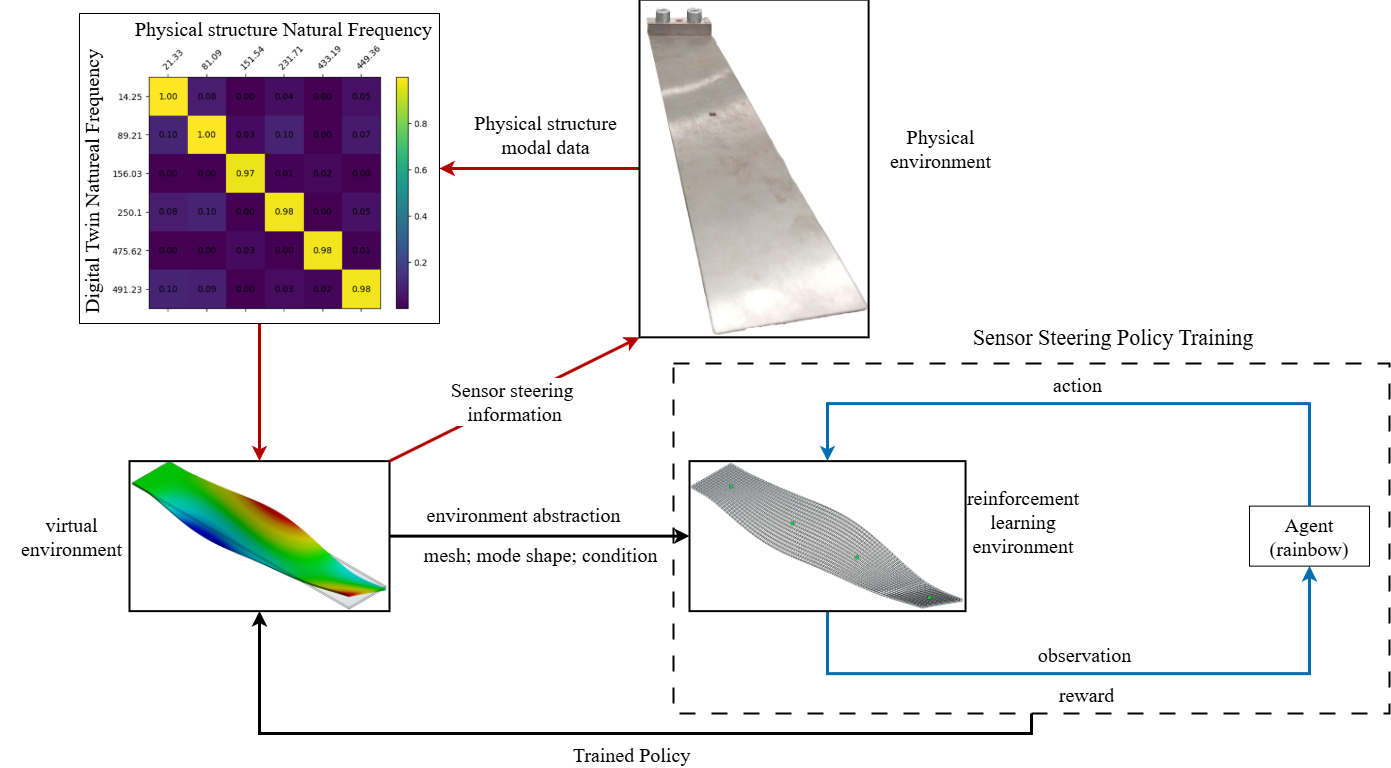 Adaptive Sensor Steering Strategy Using Deep Reinforcement Learning for Dynamic Data Acquisition in Digital TwinsCollins O Ogbodo, Timothy J Rogers, Mattia Dal Borgo, and 1 more authorProceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 2026
Adaptive Sensor Steering Strategy Using Deep Reinforcement Learning for Dynamic Data Acquisition in Digital TwinsCollins O Ogbodo, Timothy J Rogers, Mattia Dal Borgo, and 1 more authorProceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 2026This paper introduces a sensor steering methodology based on deep reinforcement learning to enhance the predictive accuracy and decision support capabilities of digital twins by optimising the data acquisition process. Traditional sensor placement techniques are often constrained by one-off optimisation strategies, which limit their applicability for online applications requiring continuous informative data assimilation. The proposed approach addresses this limitation by offering an adaptive framework for sensor placement within the digital twin paradigm. The sensor placement problem is formulated as a Markov decision process, enabling the training and deployment of an agent capable of dynamically repositioning sensors in response to the evolving conditions of the physical structure as represented by the digital twin. This ensures that the digital twin maintains a highly representative and reliable connection to its physical counterpart. The proposed framework is validated through a series of comprehensive case studies involving a cantilever plate structure subjected to diverse conditions, including healthy and damaged conditions. The results demonstrate the capability of the deep reinforcement learning agent to adaptively reposition sensors improving the quality of data acquisition and hence enhancing the overall accuracy of digital twins.
2025
-
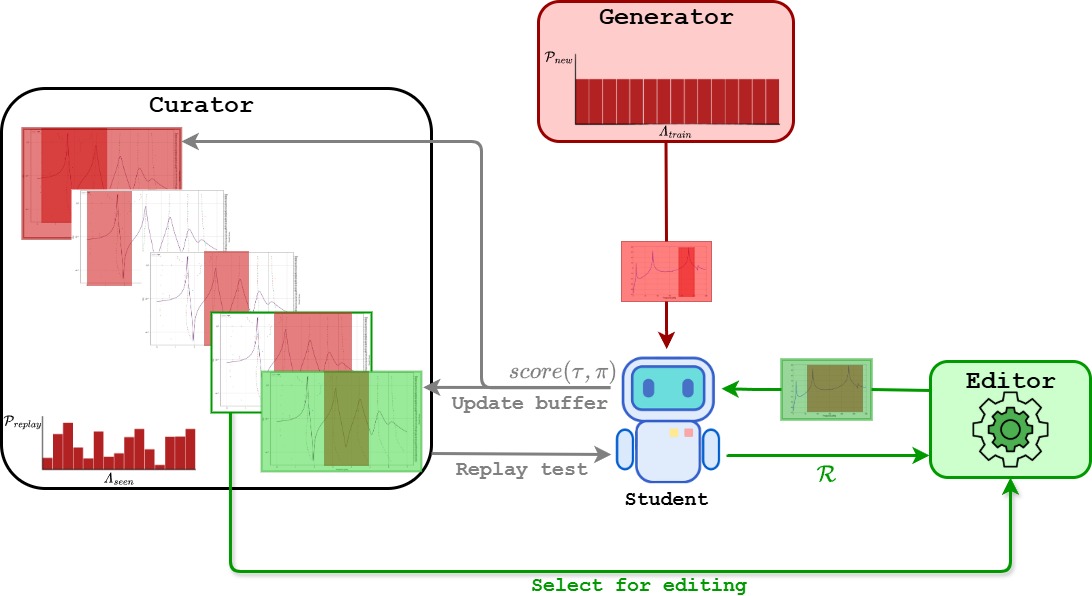 Towards Agent-based Test Support Systems: An Unsupervised Environment Design ApproachCollins O Ogbodo, Timothy J Rogers, Mattia Dal Borgo, and 1 more authorarXiv preprint arXiv:2508.14135, 2025
Towards Agent-based Test Support Systems: An Unsupervised Environment Design ApproachCollins O Ogbodo, Timothy J Rogers, Mattia Dal Borgo, and 1 more authorarXiv preprint arXiv:2508.14135, 2025Modal testing plays a critical role in structural analysis by providing essential insights into dynamic behaviour across a wide range of engineering industries. In practice, designing an effective modal test campaign involves complex experimental planning, comprising a series of interdependent decisions that significantly influence the final test outcome. Traditional approaches to test design are typically static-focusing only on global tests without accounting for evolving test campaign parameters or the impact of such changes on previously established decisions, such as sensor configurations, which have been found to significantly influence test outcomes. These rigid methodologies often compromise test accuracy and adaptability. To address these limitations, this study introduces an agent-based decision support framework for adaptive sensor placement across dynamically changing modal test environments. The framework formulates the problem using an underspecified partially observable Markov decision process, enabling the training of a generalist reinforcement learning agent through a dual-curriculum learning strategy. A detailed case study on a steel cantilever structure demonstrates the efficacy of the proposed method in optimising sensor locations across frequency segments, validating its robustness and real-world applicability in experimental settings.
2021
- Generalized oscillator model for nonlinear vibration analysis using quasi-static cubication methodAkuro Big-Alabo, Emmanuel Ogheneochuko Ekpruke, Chinwuba Victor Ossia, and 2 more authorsInternational Journal of Mechanical Engineering Education, 2021
A generalized oscillator model for nonlinear vibration analysis of various mechanical systems was proposed and solved using the quasi-static cubication method. The proposed generalized oscillator model is useful for introducing and discussing the nonlinear vibration models of several oscillatory systems. To establish the accuracy of the quasi-static cubication method for the generalized oscillator model, a number of simulations were carried out for the nonlinear vibration models of common mechanical systems derived from the generalized oscillator model. The results obtained were found to be in good agreement with exact solutions and other approximate solutions found in the literature. Furthermore, the quasi-static cubication method was found to be accurate for a wide range of oscillation amplitudes. A significant feature of the quasi-static cubication method is its simplicity and accuracy; hence, it is considered an efficient technique for nonlinear vibration analysis in undergraduate and post-graduate courses on dynamics.
2020
- Semi-analytical treatment of complex nonlinear oscillations arising in the slider-crank mechanismAkuro Big-Alabo, Collins Onyinyechukwu Ogbodo, and Chinwuba Victor OssiaWorld Scientific News, 2020
The model for the free nonlinear oscillation of the slider-crank mechanism is very complicated and difficult to solve accurately using most of the existing approximate analytical schemes. However, the continuous piecewise linearization method (CPLM), which is a recently proposed semi-analytical algorithm, is capable of producing simple and accurate periodic solutions for conservative systems irrespective of the complexity of the nonlinear restoring force. Hence, this study applied the CPLM to solve and analyze the complex nonlinear oscillations arising in the slider-crank mechanism. The CPLM results were verified using numerical solutions and it was found that the CPLM solution was accurate to less than 1.0% for angular amplitudes up to 165°. Analysis of the frequency-amplitude response revealed the existence of asymptotic behaviour as the ratio of the crank radius to the connecting rod length approaches zero or unity. Hence, oscillation models for the observed asymptotic responses were derived and found to be significantly simpler compared to the original oscillation model. Finally, analysis of the large-amplitude oscillations of the slider-crank mechanism revealed the presence of strong anharmonic response.
2019
- Dynamic analysis of crank mechanism with complex trigonometric nonlinearity: a comparative study of approximate analytical methodsAkuro Big-Alabo and Collins Onyinyechukwu OgbodoSN Applied Sciences, 2019
The geometrically nonlinear crank (GNC) is a mechanism that is found in machines. Its vibration is governed by a differential equation with complex trigonometric nonlinearity. This paper presents two approximate analytical solutions for dynamic analysis of the GNC using a quasi-static cubication method (QCM) and the energy balance method (EBM). Comparison of the results of the QCM and EBM with standard numerical results shows that the QCM gives a better estimate of the GNC vibration and captures the qualitative response better than the EBM. The study shows that the GNC exhibits a strong nonlinear vibration response at all amplitudes. The dynamic analysis also reveals an asymptotic response in the relation between the frequency and a geometrical constant defined as the ratio of the crank length to the distance between the supports of the GNC.